Table of Contents
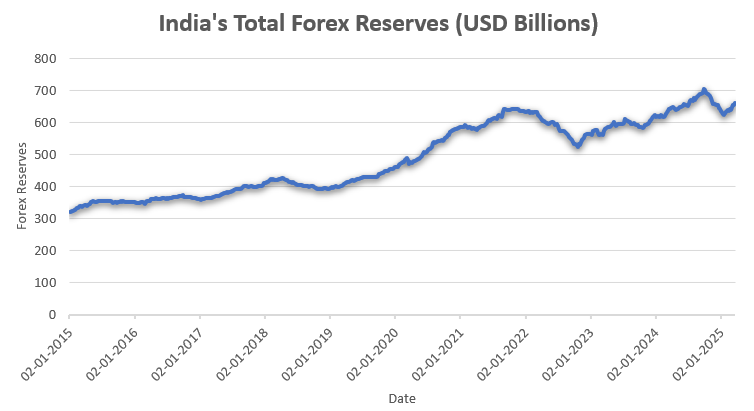
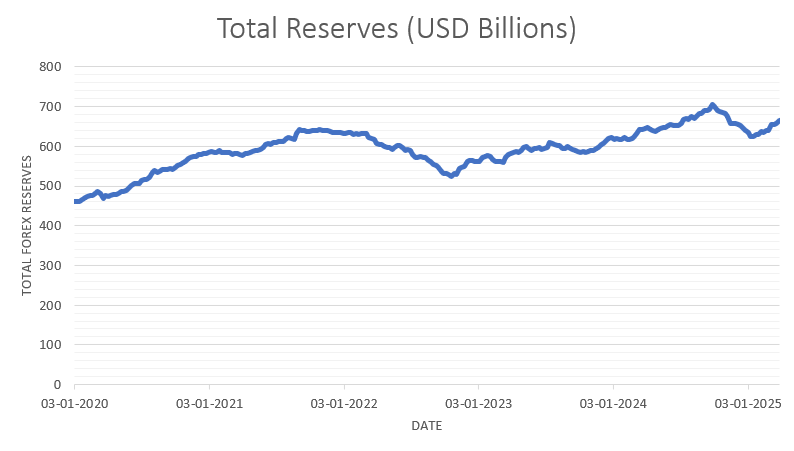
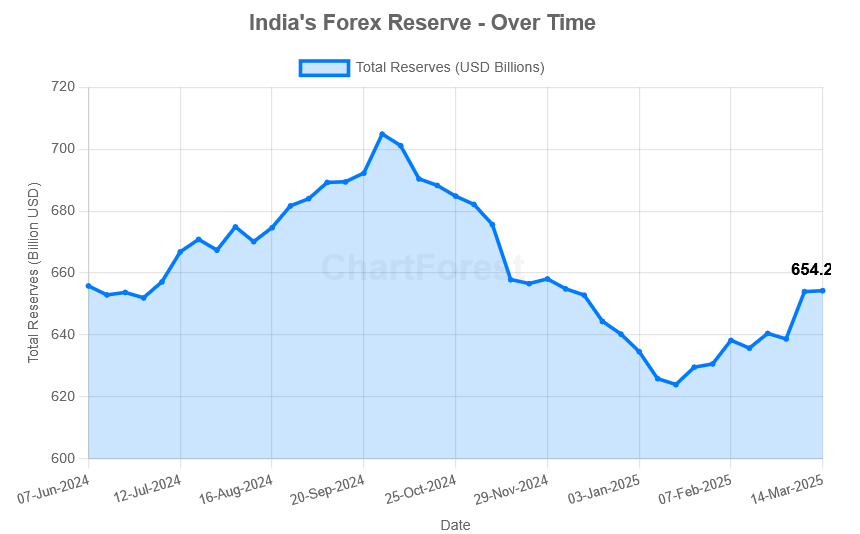
India’s foreign exchange reserves have experienced fluctuations in recent months, reflecting the dynamic nature of global financial markets and domestic economic conditions. India’s Forex Reserves stood at $654.27 billion as of March 14, 2025, marking a significant increase from the previous week. As of March 7, 2025, it was $653.97 billion.
Source: Reserve Bank of India
If you require to see the latest updates related to India’s Foreign Exchange Reserves, Please check out our page “Foreign Exchange (Forex) Reserves of India“. Data is published here as soon as the RBI publishes it.
Here is the detailed breakdown of the reserves as of March 14, 2025
According to RBI’s official report, India’s forex reserves increased last week. Below we have mentioned the detailed breakdown of the reserves:
- Foreign Currency Assets (FCA): $557.186 billion, a reduction of $96 million from the previous week of March 7, 2025.
- Gold Reserves: $74.39 billion, an increase of $66 million.
- Special Drawing Rights (SDRs): $18.26 billion, up by $51 million.
- Reserve Position in the IMF: $4.43 billion, increase by $283 million.
Managed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), these reserves consist of various assets, including foreign currency assets, gold reserves, Special Drawing Rights (SDRs), and India’s reserve position with the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
Please note that these reserves are influenced by the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) interventions in the foreign exchange market. Additionally, changes in the valuation of foreign assets due to exchange rate movements contribute to the weekly fluctuations in reserve levels.
Strong and healthy foreign exchange reserves are essential for India’s economic stability, acting as a protective measure against unforeseen external challenges, supporting the national currency, and ensuring sufficient liquidity to meet international obligations. The recent increase in the reserves highlights how strong and steady India’s economy remains despite global challenges, showing how well the RBI’s strategies are working to handle the country’s external sector.
Components of India’s Foreign Exchange Reserves
- Foreign Currency Assets (FCA): India’s total forex reserves are mainly made up of foreign currency assets, which include key global currencies like the US dollar, euro, pound sterling, and Japanese yen, with the FCA being the largest contributor.
- Gold Reserves: India keeps a good chunk of its reserves in gold, using it as a reliable safety net to tackle economic ups and downs and shifts in currency values—it’s like a comforting backup plan for tough times.
- Special Drawing Rights (SDRs): SDRs are a special kind of international reserve created by the IMF to help strengthen the official reserves of member countries.
- Reserve Position in the IMF: This highlights India’s financial support for the IMF, serving as a helpful safety net to lean on during challenging economic times.
Trends in India’s Foreign Exchange Reserves
India’s foreign exchange reserves have had their ups and downs over time, influenced by things like global economic shifts, trade patterns, foreign investments, and government decisions. They hit a record high in 2021, thanks to healthy capital inflows and a boost in global trade. Lately, though, challenges like geopolitical tensions and rising inflation have put some strain on these reserve levels.
Importance of Foreign Exchange Reserves
- Economic Stability: Having enough reserves plays a big role in keeping exchange rates steady and protecting the economy from sudden external challenges, making everything feel more stable and secure.
- Import Cover: India’s forex reserves act as a comforting safety net, making sure the country can keep up with essential imports, even during tough financial times.
- Investor Confidence: Having a strong reserve position helps build investor confidence and boosts the country’s reputation for being financially reliable.
- Intervention in Forex Markets: The RBI uses reserves to stabilize currency fluctuations and manage inflationary trends.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Even with a solid reserve position, there are still a few hurdles like growing trade deficits, capital outflows, and unpredictable global economic trends. India is working hard to address these challenges by boosting exports, drawing in foreign investments, and exploring different ways to diversify its reserve assets.