RBI Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) Rate
RBI SDF: Key Updates
Latest Release
June 6, 2025
Actual
5.25%
Previous
5.75%
Highlights
- After assessing the current and evolving macroeconomic situation, the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) decided to reduce the Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) rate to 5.25 percent, following a 50 basis point cut in the policy repo rate.
- The decision was taken during the 55th meeting of the MPC held from June 4 to 6, 2025, chaired by RBI Governor Shri Sanjay Malhotra.
- The SDF rate moves in alignment with the repo rate and acts as the floor of the liquidity adjustment facility (LAF) corridor, helping the RBI manage short-term surplus liquidity.
Reasons Behind SDF Rate Reduction (June 2025)
As per the June 2025 Monetary Policy Statement:
- Decline in Inflation: CPI inflation fell to 3.2% in April 2025, the lowest in 6 years. Food prices declined consistently for six months, and inflation expectations eased.
- Inflation Forecast: FY 2025-26 inflation is projected at 3.7%, revised down from 4%.
- Support for Growth: With GDP growth at 6.5%, below long-term potential, monetary easing supports investment and domestic demand.
- Positive Agricultural Outlook: Record Rabi harvest and an above-normal monsoon are expected to keep food inflation low.
- Global Headwinds: Ongoing geopolitical tensions and trade disruptions prompted proactive measures to stimulate internal economic momentum.
- Room for Policy Easing: With inflation under control, RBI has the flexibility to reduce both repo and SDF rates.
Expected Effects of SDF Rate Cut
- Liquidity Management: Encourages banks to lend rather than park excess funds with RBI, thereby increasing credit flow in the economy.
- Interest Rate Transmission: Helps push down short-term rates in the interbank market, aligning with broader monetary easing.
- Boost to Growth: Complements repo rate cut by easing liquidity conditions and supporting overall financial system flexibility.
- Inflation Control Maintained: Despite easing, inflation remains well within the RBI’s comfort zone of 4% (+/-2%).
Historical RBI Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) Rate Chart
SDF Rate Chart (RBI) - Historical & Current Trends
RBI Policy Rates & Ratios
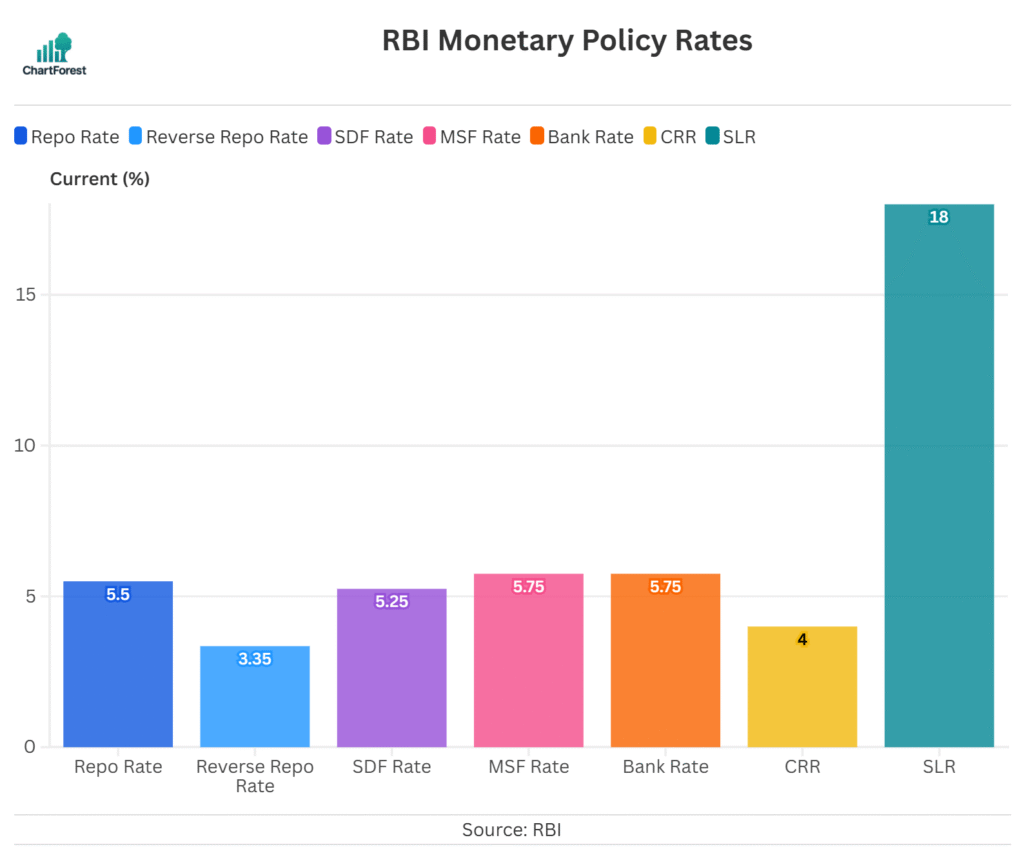
RBI Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) Rate overview
SDF was Introduced by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on April 8, 2022. It is a monetary policy tool that allows commercial banks (both govt and private) to deposit excess/extra funds with the RBI without collateral. The main purpose of the SDF is to absorb surplus liquidity from the banking system, as it helps the RBI regulate inflation and improve monetary policy effectiveness.
Importance of RBI Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) policy
- Manage Liquidity: Enables commercial banks a secure and profitable way to temporarily deposit surplus funds with the RBI.
- Collateral-Free Deposits: Unlike other liquidity management tools like Reverse Repo, SDF does not require collateral. Therefore, it gives RBI more flexibility in liquidity absorption.
- Control Inflation: By absorbing excess liquidity from the market, SDF helps in preventing inflationary pressures.
- Helps alongside other tools: It works alongside other tools like the repo rate, reverse repo rate, CRR, MSF, and open market operations to improve the RBI’s control over liquidity.
- Stability: It also helps RBI to maintain price stability and support economic growth.
- Reduces volatility: It also helps reduce volatility in the money market and enhances overall stability.
FAQs
What is the Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) and why is it important?
The Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) is a handy tool introduced by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to manage surplus funds in the banking system. Basically, it gives banks a simple way to park their extra money with the RBI and earn interest, all without needing to provide any security or collateral.
How is SDF different from the reverse repo rate?
Both the Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) and the reverse repo rate help the RBI manage excess cash from banks, but there’s a key distinction between the two. The reverse repo rate requires banks to provide government securities as collateral, while SDF is much simpler—banks can park their money safely with the RBI without needing to deal with paperwork or pledging assets.
How does SDF affect interest rates and RBI’s policies?
SDF is a tool the RBI uses to make sure its interest rate decisions, like changes to the repo rate, have the right impact on the economy. You see, when there’s too much money floating around, loan rates might stay low even if RBI hikes the repo rate. With the SDF, RBI can soak up that extra cash, helping market rates align better with its policy goals.
How does SDF affect the stock market?
For investors, the SDF can give clues about RBI’s plans. If the RBI uses SDF more often, it could mean tighter money policy, possibly leading to higher loan rates and slower growth—this may affect stock prices. Also, absorbing liquidity through SDF can reduce market funds, which may lead to lower trading activity.
How can investors track the SDF for better decisions?
Investors should follow RBI updates on SDF usage and any changes in its rate. Seeing how frequently the RBI uses SDF and the amounts involved can clue you in on whether they’re tightening or easing monetary policy. Pair that with economic news and global trends, and you’ll have some solid insights to make smarter decisions.
Related Indicators
Important
If you notice any discrepancies in the data or find any inaccuracies, please let us know. We will review and correct them as soon as possible.
Other Indicators
Inflation and Price Indicators
- Inflation Rate
- Consumer Price Index
- Wholesale Price Index
- Food Inflation (CFPI)
- Health Inflation
- Education Inflation
- CPI Housing Utilities
- Inflation Expectations
GDP & Economic Growth Indicator
- GDP
- Full Year GDP Growth
- GDP per Capita
- GDP from Agriculture
- GDP from Construction
- Goods and Services Tax (GST) Revenue
- Imports
- Exports
