RBI Repo Rate Policy
RBI's Repo Rate: Key Updates
Latest Release
June 6, 2025
Actual
5.5%
Previous
6%
Highlight
- After assessing the current and evolving macroeconomic situation, the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) decided to reduce the policy repo rate by 50 basis points to 5.50 percent with immediate effect.
- The decision was taken during the 55th meeting of the MPC held from June 4 to 6, 2025, under the chairmanship of RBI Governor Shri Sanjay Malhotra.
Reasons for the Repo Rate Cut by RBI (June 2025)
As per the June 2025 Monetary Policy Statement:
- Decline in Inflation: CPI inflation dropped to 3.2% in April 2025, a 6-year low, food inflation fell for six straight months, Core inflation remained stable and contained, and inflation forecast for FY 2025-26 was lowered to 3.7% (from 4%).
- Need to Support Growth: Although GDP is growing at 6.5%, it’s below potential and the global outlook remains weak, rate cuts aim to stimulate private consumption and investment.
- Favourable Agricultural Outlook: Record Rabi crop output and above-normal monsoon forecast.
- Global Economic Uncertainty: Trade tensions and geopolitical risks may affect exports and investment. RBI wants to proactively support domestic demand.
- Monetary Space Available: Since inflation was within target and moderating, RBI had room to use monetary easing.
Expected Effects of the Rate Cut
- Home/Car Loans: Cheaper EMIs due to lower interest rates.
- Business Loans: Boost in investment and capital spending.
- Stock Market: Positive sentiment due to growth focus.
- Consumer Demand: More spending due to lower borrowing costs.
Historical RBI's Repo Rate Data Chart
Repo Rate Chart (RBI) - Historical & Current Trends
RBI Policy Rates & Ratios
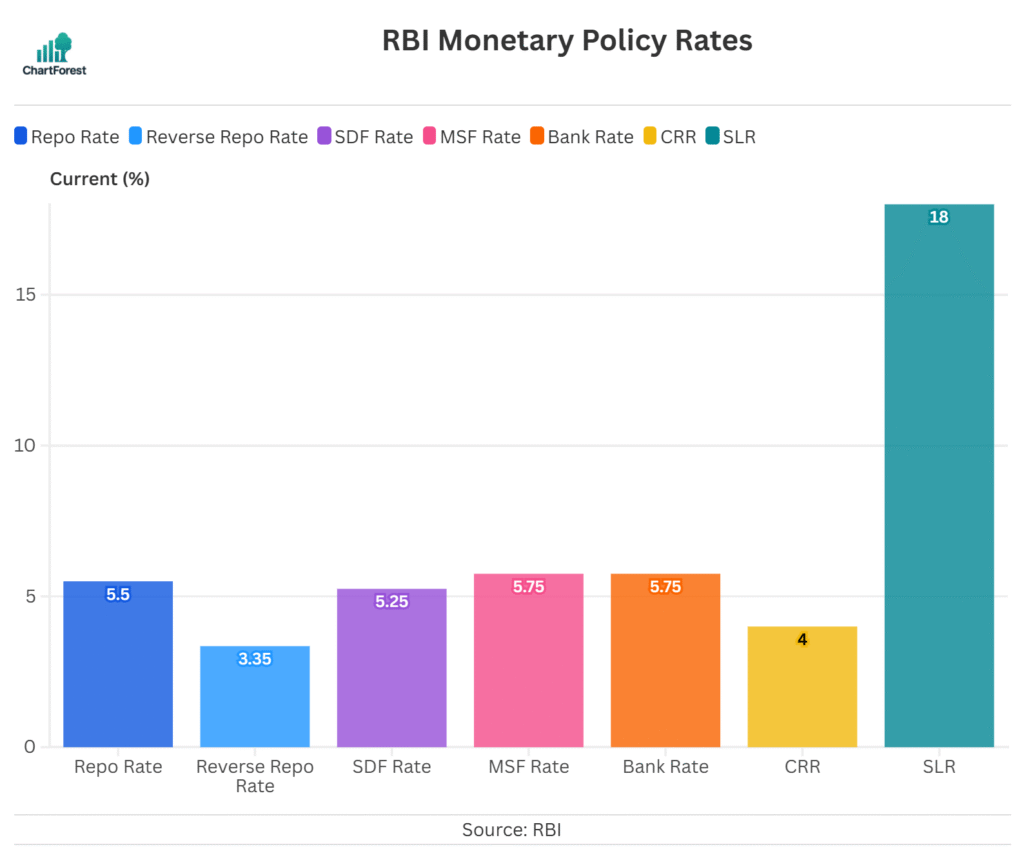
RBI Repo Rate overview
Repo Rate is the interest rate at which the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) lends money to commercial banks (both govt and private) when they need funds.
So, how does the Repo Rate work?
When banks need money, they approach the RBI and borrow by using govt securities as collateral. They (banks) pay interest (according to the repo rate) on the borrowed amount to the RBI. Therefore, when the repo rate changes, it affects loan interest rates, inflation, and economic growth.
RBI Repo Rate Change Impact
What happens when RBI cuts the Repo Rate:
- Banks can borrow money more easily from the RBI.
- Loan interest rates drop, and it makes borrowing cheaper for consumers.
- More and more people take loans, increasing spending and stimulating the economy.
What happens when RBI increases the Repo Rate:
- Banks pay more to borrow from the RBI, making loans expensive.
- Fewer people take loans, reducing the money supply in the market.
- Helps control inflation by slowing down excessive spending.
FAQs
What is the repo rate and how does it work?
The Repo Rate is basically the interest rate the RBI charges when lending money to banks for a short time. To make this happen, banks hand over government-approved securities as collateral, with an agreement to repurchase them later. It’s a handy way for banks to cover their short-term cash needs.
How are the repo and reverse repo rates related?
The Repo Rate is essentially what commercial banks pay to borrow money from the RBI, while the reverse repo rate is what they earn when they deposit extra funds with the RBI. Usually, the repo rate is higher than the reverse repo rate.
How does a change in the repo rate affect your loans?
Loans tied to the repo rate are closely connected to changes in the RBI’s benchmark lending rate. When the repo rate drops, it’s good news for borrowers—it often means banks will lower their lending rates, which could bring down interest rates and make your monthly EMIs a bit lighter. On the flip side, if the repo rate climbs higher, those with repo-linked loans might see their interest rates and EMIs go up faster than loans tied to other benchmarks.
How does the repo rate affect the stock market?
When repo rates are higher, it can cool down business growth and squeeze company profits, which might put some pressure on the stock market. On the flip side, lower rates make borrowing simpler, often giving the market a nice little boost.
Why does the RBI use the repo rate?
The RBI tweaks the repo rate to keep inflation in check and guide the flow of money in the economy. When the rate goes up, it helps cool off spending to manage inflation, and when it’s lowered, it nudges borrowing and boosts growth.
Related Indicators
Important
If you notice any discrepancies in the data or find any inaccuracies, please let us know. We will review and correct them as soon as possible.
Other Indicators
Inflation and Price Indicators
- Inflation Rate
- Consumer Price Index
- Wholesale Price Index
- Food Inflation (CFPI)
- Health Inflation
- Education Inflation
- CPI Housing Utilities
- Inflation Expectations
GDP & Economic Growth Indicator
- GDP
- Full Year GDP Growth
- GDP per Capita
- GDP from Agriculture
- GDP from Construction
- Goods and Services Tax (GST) Revenue
- Imports
- Exports
